#90DaysofDevops challenge
- Write a bash script createDirectories1.sh that when the script is executed with three given arguments (one is the directory name and second is the start number of directories and the third is the end number of directories ) it creates a specified number of directories with a dynamic directory name.
Input=

Output=

2. Create a Script to back up all your work done till now.
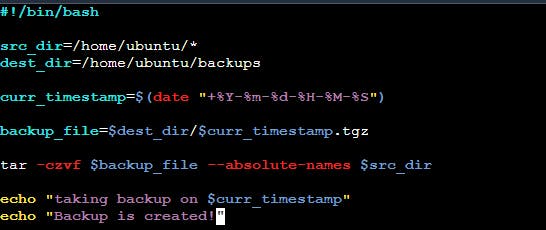
3. Read About Cron and Crontab, to automate the Script
Cron is the system's main scheduler for running jobs or tasks unattended. A command called crontab allows the user to submit, edit or delete entries to cron. A crontab file is a user file that holds the scheduling information.
You can use the following command to check the crontab list :-
crontab -l
If you want to create a new cron job you use the following command and enter in text editor to add a new cron entry.
crontab -e
It is possible to create jobs that you want to reoccur. This process is known as job scheduling. This process is handled by the cron service or a daemon called crond. and crontab -r to remove the current crontab configuration.
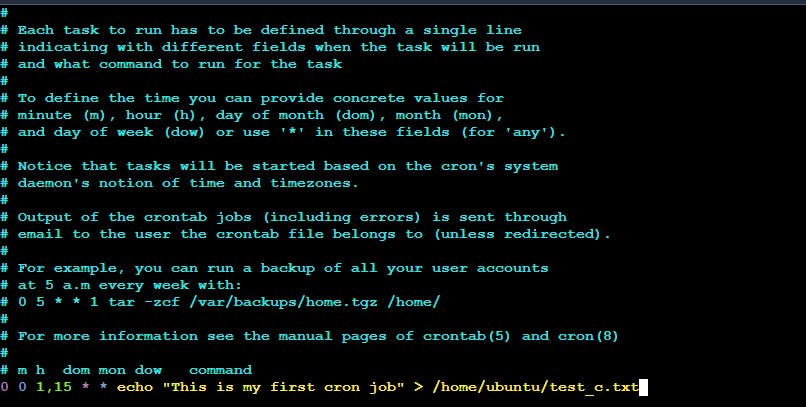
0 0 1, 15 * * is a cron pattern which indicates that this particular command should run on 1st and 15th date of every month at 00:00 and output of the script will be appended to the test_c.txt file.
4. Read about User Management
User is an entity that can manipulate files and perform serveral other operations. Each user in a Linux operating system is assigned an id. After installation of the OS, ID 0 is assigned to the root user. ID 1–999 are assigned to system users and ID from 1000 onwards are assigned to local user.
1. Command to get id of a user
id username
2.Command to add a user
sudo useradd username
3.Command to assign password to a user
passwd username
4.Command to access user configuration
cat /etc/passwd
5.Command to delete a user
userdel -r username
6.For switching user account
su username
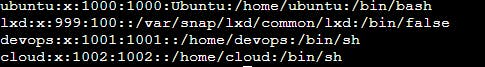
5. Create 2 users and just display their Username
Added 2 users:

To display their names we are going to use the following command:
cat /etc/passwd
Thank you for reading! Happy Learning!!
sayali